Embark on a journey into the realm of chemistry as we delve into the electron dot diagram of neon, a captivating representation of this noble gas’s electron configuration. This visual tool unveils the secrets of neon’s chemical properties and behavior, providing a deeper understanding of its unique characteristics.
Neon, with its distinctive electron configuration, stands out among the elements. Its electron dot diagram, a graphical representation of its electron arrangement, offers a window into its chemical nature, revealing the reasons behind its exceptional stability and inertness.
Neon’s Electron Configuration
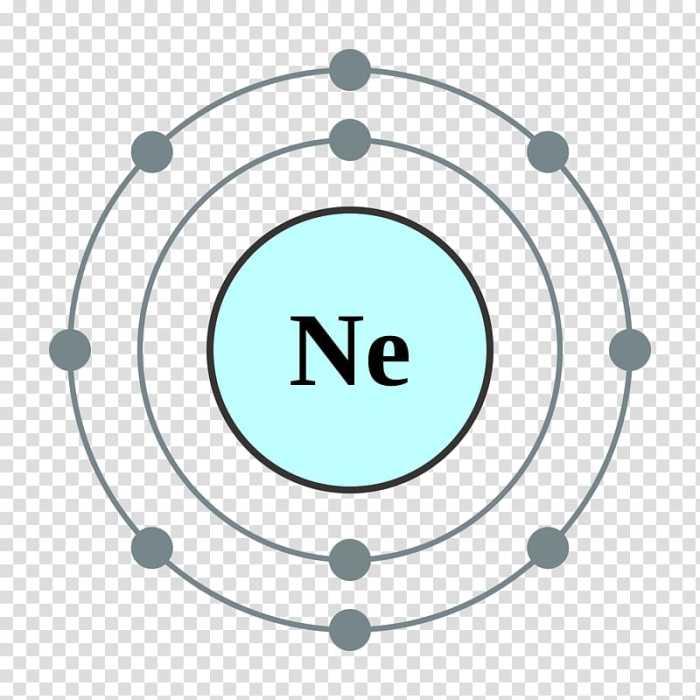
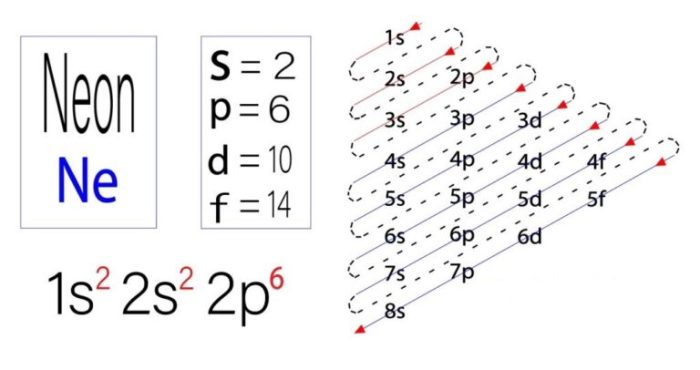
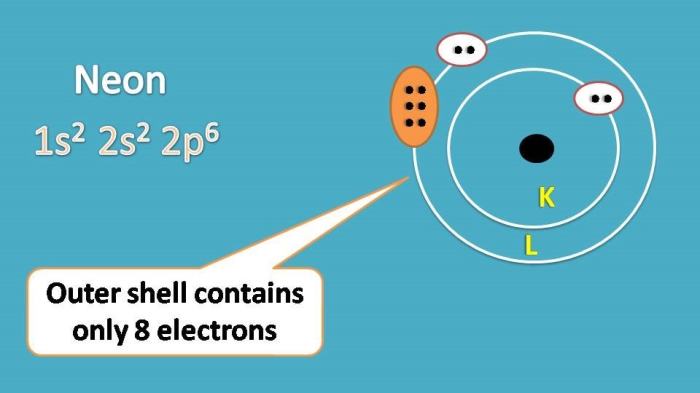
Neon is a noble gas with the atomic number 10. Its electron configuration is 1s 22s 22p 6. This means that neon has two electrons in its first energy level, two electrons in its second energy level, and six electrons in its third energy level.
Significance of Neon’s Electron Configuration
Neon’s electron configuration is significant because it makes neon a very stable element. The eight electrons in neon’s outermost energy level create a complete shell, which makes neon unreactive with other elements. This is why neon is a noble gas.
Electron Dot Diagram of Neon
The electron dot diagram of an element is a representation of the arrangement of its valence electrons in the outermost energy level. It provides a visual understanding of the element’s electron configuration and chemical reactivity.
Drawing the Electron Dot Diagram of Neon
To draw the electron dot diagram of neon, follow these steps:
- Write the chemical symbol for neon, Ne.
- Determine the number of valence electrons for neon. Neon has 8 electrons, so it has 8 valence electrons.
- Place two dots next to the chemical symbol to represent the two valence electrons in the outermost energy level.
- Continue adding dots in pairs until all 8 valence electrons are represented.
Explanation of the Electron Dot Diagram
The electron dot diagram of neon shows that it has two valence electrons in the outermost energy level. This arrangement is stable and unreactive because the outermost energy level is full. Neon is a noble gas and does not readily form chemical bonds with other elements.
Valence Electrons in Neon
In the realm of chemistry, valence electrons play a pivotal role in determining the chemical behavior and bonding capabilities of elements. These are the electrons that reside in the outermost energy level of an atom, and they are the ones primarily involved in chemical reactions.
Number of Valence Electrons in Neon
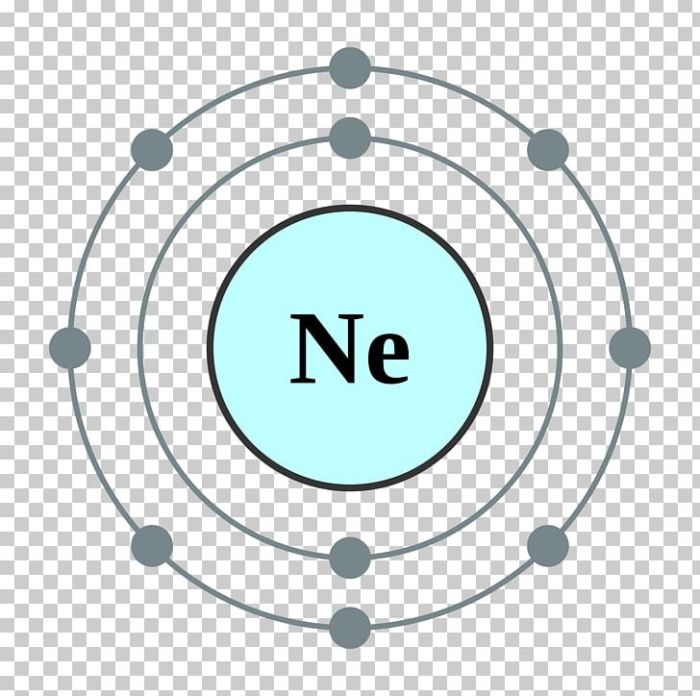
Neon, an element with the atomic number 10, possesses a total of 10 electrons. According to the Aufbau principle, these electrons are arranged in specific energy levels or shells. The first two shells are filled with 2 and 8 electrons, respectively, leaving 2 electrons in the outermost shell.
These 2 outermost electrons are the valence electrons of neon.
Neon’s electron dot diagram depicts its atomic structure, with its eight valence electrons forming a stable octet. Understanding this diagram is crucial for various chemical concepts. For instance, in cell G6 of a spreadsheet, you can enter a formula to calculate the number of valence electrons based on the electron dot diagram.
By referencing the in cell g6 enter a formula guide, you can explore this formula and its applications, further enhancing your understanding of electron dot diagrams and their significance in chemistry.
Role of Valence Electrons in Chemical Bonding
Valence electrons are the key players in chemical bonding. They determine the chemical properties of an element and its ability to form bonds with other atoms. In the case of neon, the presence of 2 valence electrons makes it a stable and unreactive element.
Neon atoms have a complete valence shell, meaning they have a full complement of electrons in their outermost energy level. This stable electron configuration makes neon reluctant to participate in chemical reactions and form bonds with other atoms. As a result, neon is often referred to as an inert gas or a noble gas.
Chemical Properties of Neon

Neon is a noble gas, meaning it is highly unreactive and does not readily form chemical bonds with other elements. This is due to its electron configuration, which has a full valence shell of eight electrons. A full valence shell makes neon stable and unlikely to participate in chemical reactions.
Chemical Inertness of Neon
Neon’s chemical inertness has been demonstrated in various experiments and observations. For instance, it does not react with most other elements, even at high temperatures. Additionally, it does not form compounds with other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen.
Applications of Neon
Neon has a wide range of applications due to its unique properties, including its low reactivity, high electrical conductivity, and distinctive orange-red glow.
Lighting and Illumination
Neon’s most well-known application is in lighting, particularly in the iconic neon signs that have become a hallmark of cities and businesses. Neon’s bright, eye-catching glow is produced when an electric current passes through a neon-filled glass tube. The color of the light can be varied by adding different gases or phosphors to the tube.
Top FAQs: Electron Dot Diagram Of Neon
What is the electron configuration of neon?
Neon has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6, with two electrons in each of its three energy levels.
How many valence electrons does neon have?
Neon has eight valence electrons, which occupy the outermost energy level.
Why is neon a noble gas?
Neon is a noble gas because its electron configuration is stable, with a full outermost energy level. This stability makes it unreactive with other elements.