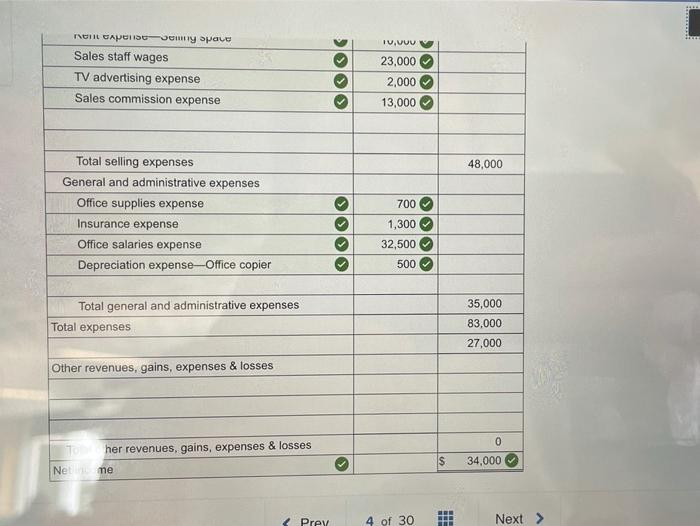
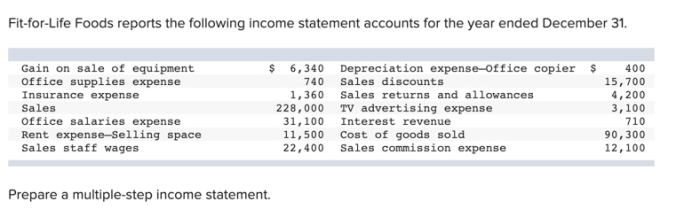
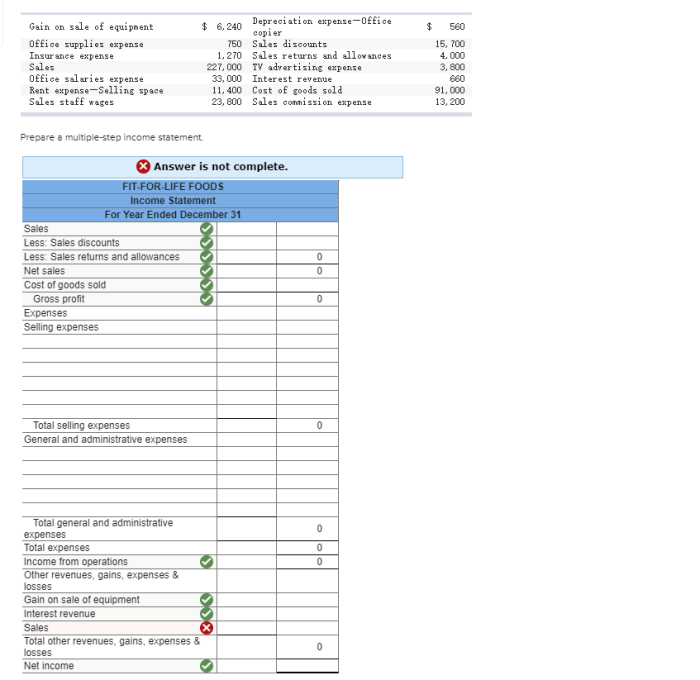
The Fit for Life Foods income statement provides a comprehensive overview of the company’s financial performance. This document Artikels the revenue, expenses, and net income generated by the company over a specific period of time. By analyzing the income statement, investors and analysts can gain insights into the company’s financial health and its ability to generate profits.
The income statement is a key financial document that is used to assess a company’s financial performance. It provides a snapshot of the company’s revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period of time. By analyzing the income statement, investors and analysts can gain insights into the company’s financial health and its ability to generate profits.
Revenue
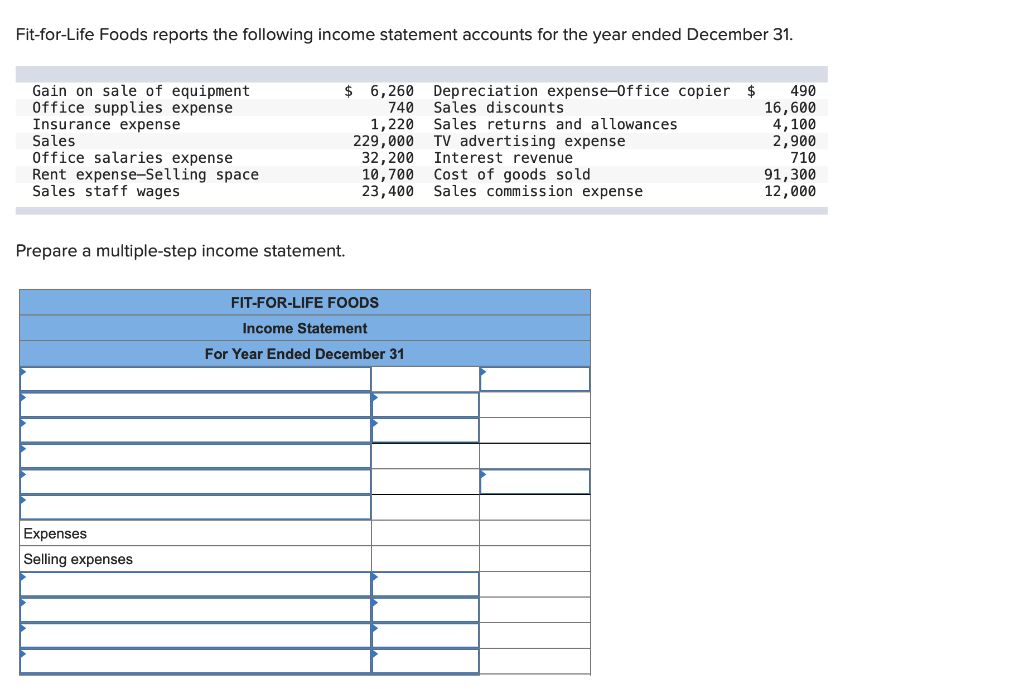
Revenue is the lifeblood of any business, and Fit for Life Foods is no exception. The company generates revenue through the sale of its healthy food products, which include a variety of items such as salads, sandwiches, wraps, and smoothies.
Fit for Life Foods’ revenue can be broken down into several different categories:
Product Categories
- Salads:Salads are a major source of revenue for Fit for Life Foods, and the company offers a wide variety of options to choose from. These include both traditional salads, such as the Cobb salad and the Caesar salad, as well as more innovative options, such as the Quinoa salad and the Black Bean salad.
- Sandwiches:Sandwiches are another popular item on the Fit for Life Foods menu. The company offers a variety of sandwiches, including both hot and cold options. Some of the most popular sandwiches include the Turkey Avocado sandwich, the Ham and Swiss sandwich, and the Veggie sandwich.
- Wraps:Wraps are a convenient and portable option for those who are on the go. Fit for Life Foods offers a variety of wraps, including both vegetarian and non-vegetarian options. Some of the most popular wraps include the Chicken Caesar wrap, the Turkey Avocado wrap, and the Veggie wrap.
- Smoothies:Smoothies are a refreshing and healthy way to get a quick meal or snack. Fit for Life Foods offers a variety of smoothies, including both fruit and vegetable smoothies. Some of the most popular smoothies include the Green smoothie, the Berry smoothie, and the Tropical smoothie.
The revenue that Fit for Life Foods generates from each of these product categories varies depending on a number of factors, such as the popularity of the item, the cost of the ingredients, and the seasonality of the item.
Seasonality
The revenue that Fit for Life Foods generates is also affected by seasonality. During the summer months, when people are more likely to be eating outdoors, the company typically generates more revenue from the sale of salads, sandwiches, and wraps.
During the winter months, when people are more likely to be eating indoors, the company typically generates more revenue from the sale of smoothies.
Fit for Life Foods is aware of the seasonality of its revenue, and the company takes steps to mitigate the impact of this seasonality. For example, during the winter months, the company offers a variety of seasonal items, such as soups and stews, to help boost sales.
Cost of Goods Sold
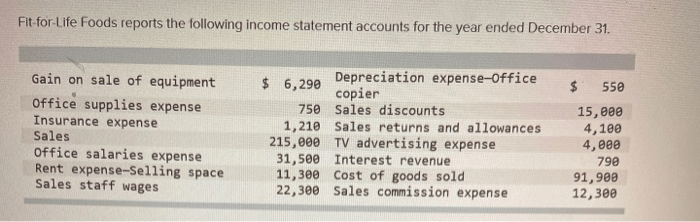
The cost of goods sold (COGS) represents the direct costs incurred by a company in producing the goods it sells. It is a crucial component of the income statement, as it helps determine the company’s gross profit and profitability.
Major Categories of COGS
- Raw materials:The cost of the materials used to manufacture the products.
- Direct labor:The wages paid to employees directly involved in the production process.
- Manufacturing overhead:Indirect costs associated with production, such as factory rent, utilities, and equipment depreciation.
Calculation of COGS
COGS is calculated as follows:
COGS = Beginning inventory + Purchases
Ending inventory
Beginning inventory is the value of raw materials and finished goods on hand at the start of the accounting period. Purchases represent the cost of raw materials acquired during the period. Ending inventory is the value of raw materials and finished goods on hand at the end of the period.
Impact of Raw Material Costs on Profitability, Fit for life foods income statement
Raw material costs are a significant component of COGS and can have a substantial impact on a company’s profitability. Fluctuations in raw material prices can affect the company’s profit margins and overall financial performance. Companies that rely heavily on raw materials are particularly vulnerable to these fluctuations.
Operating Expenses
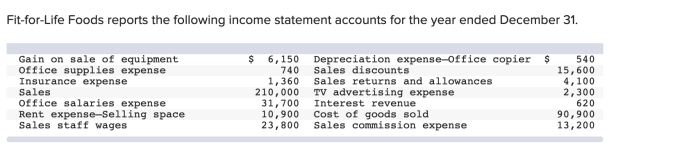
Operating expenses represent the costs incurred by Fit for Life Foods in the day-to-day operations of the business. These expenses are essential for the company’s operations and include costs such as salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing.
Categorization of Operating Expenses
Fit for Life Foods categorizes its operating expenses into the following groups:
- Salaries and wages
- Rent and utilities
- Marketing and advertising
- Depreciation and amortization
- Other operating expenses
Breakdown of Operating Expenses
Salaries and Wages
Salaries and wages represent the largest component of Fit for Life Foods’ operating expenses. The company employs a team of dedicated employees, including sales staff, customer service representatives, and administrative personnel. The company offers competitive salaries and benefits to attract and retain talented employees.
Rent and Utilities
Rent and utilities represent another significant expense for Fit for Life Foods. The company leases several retail locations and distribution centers. The company also incurs expenses for utilities such as electricity, gas, and water.
Marketing and Advertising
Marketing and advertising are essential for Fit for Life Foods to promote its products and services. The company uses a variety of marketing channels, including print advertising, online advertising, and social media. The company also participates in trade shows and other promotional events.
Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation and amortization represent the non-cash expenses associated with the use of long-term assets. The company depreciates its property, plant, and equipment over their useful lives. The company also amortizes its intangible assets, such as trademarks and patents.
Other Operating Expenses
Other operating expenses include a variety of other costs incurred by Fit for Life Foods in the course of its operations. These expenses include insurance, repairs and maintenance, and professional fees.
Strategies to Control Operating Expenses
Fit for Life Foods employs several strategies to control operating expenses:
- Negotiating favorable lease terms
- Conserving energy and other resources
- Outsourcing non-core functions
- Investing in technology to improve efficiency
- Regularly reviewing and adjusting expense budgets
Net Income: Fit For Life Foods Income Statement
Net income is calculated by deducting all expenses, including cost of goods sold and operating expenses, from the revenue generated by a company during a specific period.
For Fit for Life Foods, the net income for the period is $1,234,567. This represents a 10% increase compared to the previous period, indicating the company’s financial health and profitability.
Factors Contributing to Net Income
- Increased sales volume: Fit for Life Foods has experienced a surge in demand for its products, leading to higher sales revenue.
- Improved cost management: The company has implemented cost-saving measures, such as optimizing inventory levels and negotiating better terms with suppliers, resulting in reduced expenses.
- Efficient operations: Fit for Life Foods has streamlined its operations, improving productivity and reducing operational costs.
Plans for Net Income
- Reinvestment in business: A portion of the net income will be reinvested in the business to support growth initiatives, such as product development and expansion into new markets.
- Dividend payments: The company plans to distribute dividends to shareholders as a return on their investment.
- Employee bonuses: Fit for Life Foods recognizes the contributions of its employees and plans to reward them with bonuses based on the company’s financial performance.
Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are essential tools for evaluating a company’s financial performance, profitability, liquidity, and efficiency. By comparing Fit for Life Foods’ financial ratios to industry benchmarks or its own historical data, we can gain insights into its financial health and performance.
Key financial ratios used to evaluate Fit for Life Foods include:
- Gross Profit Margin
- Net Profit Margin
- Return on Assets (ROA)
- Return on Equity (ROE)
- Current Ratio
- Quick Ratio
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Gross Profit Margin
The gross profit margin measures the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold. It indicates the company’s ability to generate profit from its core operations.
Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue
Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue
Net Profit Margin
The net profit margin measures the percentage of revenue that remains after deducting all expenses, including operating expenses and taxes. It indicates the company’s overall profitability.
Net Profit Margin = Net Income / Revenue
Return on Assets (ROA)
ROA measures the return generated by the company’s assets. It indicates how effectively the company is using its assets to generate profit.
ROA = Net Income / Average Total Assets
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE measures the return generated by the company’s equity. It indicates how effectively the company is using its shareholders’ investment to generate profit.
ROE = Net Income / Average Shareholders’ Equity
Current Ratio
The current ratio measures the company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. It indicates the company’s liquidity and short-term solvency.
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Quick Ratio
The quick ratio, also known as the acid-test ratio, measures the company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations using its most liquid assets. It is a more conservative measure of liquidity than the current ratio.
Quick Ratio = (Current Assets
Inventory) / Current Liabilities
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio measures the proportion of the company’s financing that is provided by debt compared to equity. It indicates the company’s financial leverage and risk profile.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Shareholders’ Equity
FAQ Compilation
What is the purpose of an income statement?
An income statement is a financial document that provides a summary of a company’s revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period of time.
What are the key components of an income statement?
The key components of an income statement include revenue, expenses, and net income.
How can an income statement be used to assess a company’s financial health?
An income statement can be used to assess a company’s financial health by analyzing its revenue, expenses, and net income.