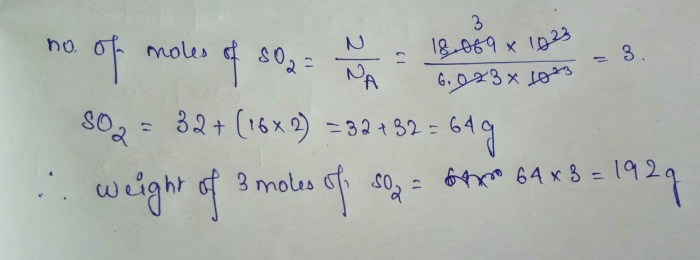The concept map of matter in chemistry serves as a roadmap to understanding the fundamental principles that govern the physical and chemical behavior of matter. Delving into this map, we embark on a journey that unravels the mysteries of matter’s composition, structure, and interactions.
From defining matter and its diverse states to exploring the intricate world of chemical bonding and molecular architecture, this guide illuminates the essential concepts that underpin chemistry. We delve into the dynamics of states of matter and phase transitions, unraveling the factors that drive these transformations.
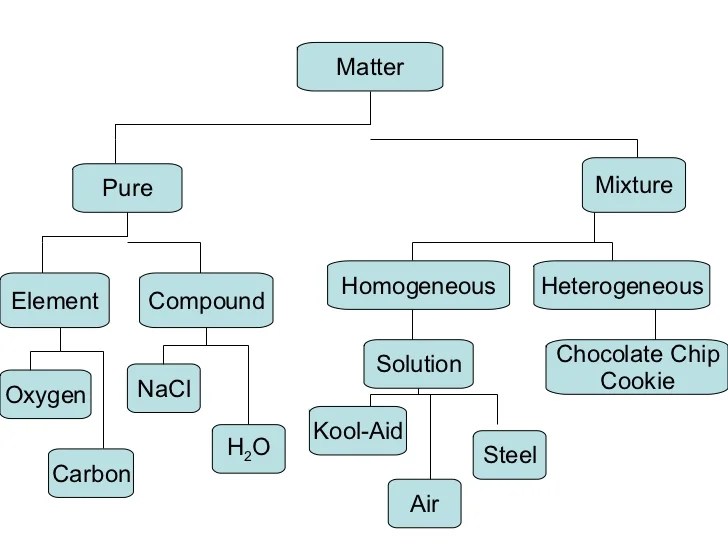
1. Matter and Its Properties: Concept Map Of Matter In Chemistry
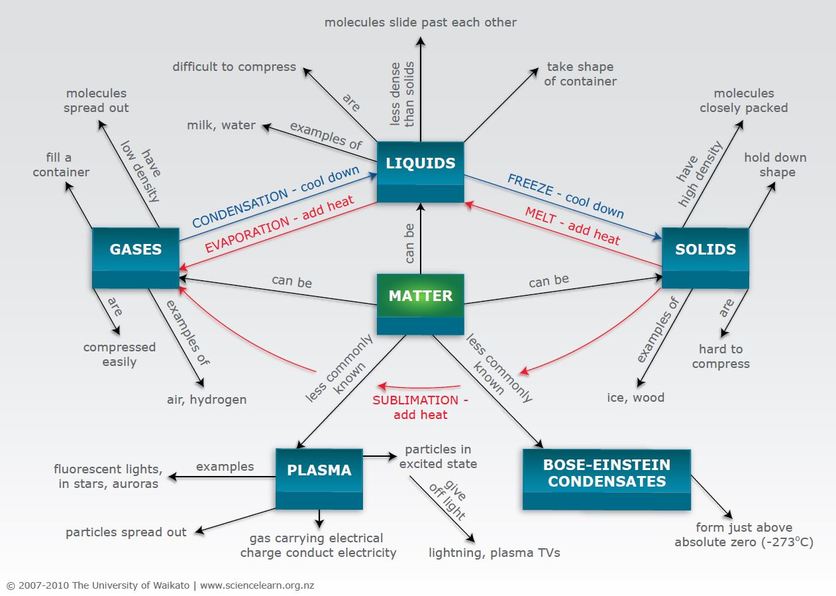
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape, and gases have no definite shape or volume.Physical
properties are characteristics that can be observed without changing the composition of matter, such as color, density, and melting point. Chemical properties describe how matter reacts with other substances, such as flammability and reactivity.
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Chemical bonding is the force that holds atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are three main types of chemical bonds: covalent, ionic, and metallic. Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons, ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred from one atom to another, and metallic bonds form when metal atoms share electrons in a sea of electrons.Molecules
are formed when two or more atoms are bonded together. Molecular structure refers to the arrangement of atoms within a molecule.
States of Matter and Phase Transitions
The different states of matter are solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Phase transitions occur when matter changes from one state to another, such as when ice melts to become water. Phase transitions can be caused by changes in temperature, pressure, or both.
Chemical Reactions and Energy
Chemical reactions are processes in which substances are transformed into new substances. There are many different types of chemical reactions, including synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, and double displacement reactions.Chemical energy is the energy stored in the bonds between atoms. Chemical reactions can release or absorb energy, depending on the type of reaction.
Applications of Chemistry in Real-Life, Concept map of matter in chemistry
Chemistry is applied in many different fields, including medicine, materials science, and environmental science. Chemistry has led to the development of new drugs, materials, and technologies that have improved our lives. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks of chemical applications and to use them responsibly.
Query Resolution
What is the concept map of matter in chemistry?
The concept map of matter in chemistry is a visual representation of the fundamental concepts and relationships that govern the behavior of matter.
What are the different states of matter?
The three primary states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. Plasma is a fourth state of matter that occurs at extremely high temperatures.
What is chemical bonding?
Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms or molecules interact to form new substances. The three main types of chemical bonds are covalent, ionic, and metallic.