Treble clef ledger lines answer key provides a comprehensive overview of the concept, identification, and application of ledger lines in treble clef music notation. This guide explores the rules, exercises, and examples to enhance understanding and proficiency in reading and writing music with treble clef ledger lines.
The following sections delve into the intricacies of treble clef ledger lines, equipping musicians with the knowledge and skills to navigate musical scores with confidence.
1. Treble Clef Ledger Lines Overview

Ledger lines are short, horizontal lines added above or below the staff in music notation. In the treble clef, ledger lines are used to extend the range of notes that can be written.
Treble clef ledger lines serve two main purposes: to extend the range of notes above the staff for high-pitched instruments like the flute or piccolo, and to extend the range of notes below the staff for low-pitched instruments like the bassoon or tuba.

2. Identifying Notes on Treble Clef Ledger Lines
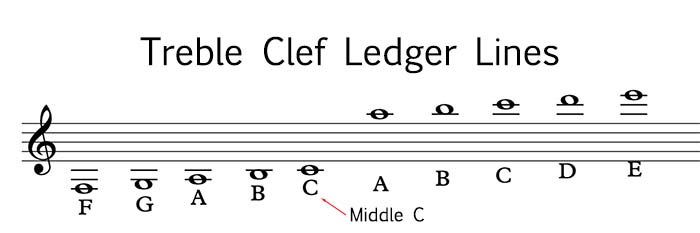
To identify notes on treble clef ledger lines, follow these rules:
- Ledger lines above the staff are counted up from the top line of the staff.
- Ledger lines below the staff are counted down from the bottom line of the staff.
- The note name of the ledger line is the same as the note name of the line or space it intersects.
Here is an interactive exercise to practice identifying notes on ledger lines:
The following table summarizes the note names for each ledger line:
| Ledger Line | Note Name |
|---|---|
| 1st above | E |
| 2nd above | F |
| 3rd above | G |
| 1st below | C |
| 2nd below | B |
| 3rd below | A |
3. Reading Music with Treble Clef Ledger Lines
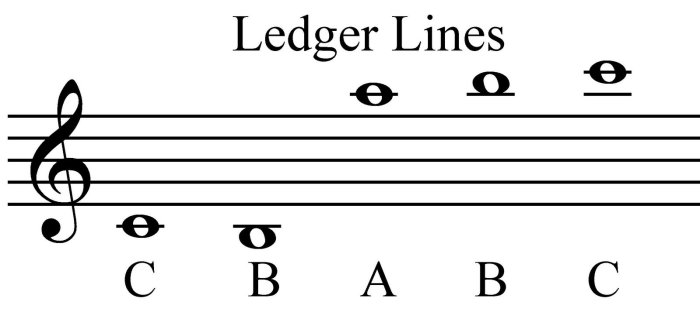
Reading music with treble clef ledger lines is essential for playing instruments that extend beyond the range of the staff. To read music with ledger lines, simply apply the rules for identifying notes on ledger lines to the music you are reading.
Here are some examples of musical passages that use treble clef ledger lines:
- Flute music often uses ledger lines above the staff to reach high notes.
- Bassoon music often uses ledger lines below the staff to reach low notes.
- Piano music can use ledger lines to extend the range of notes in both the treble and bass clefs.
4. Writing Music with Treble Clef Ledger Lines: Treble Clef Ledger Lines Answer Key

To write music with treble clef ledger lines, follow these rules:
- Ledger lines above the staff are written as short, horizontal lines extending up from the top line of the staff.
- Ledger lines below the staff are written as short, horizontal lines extending down from the bottom line of the staff.
- The note head is placed on the ledger line that corresponds to the note name.
The following table summarizes the ledger lines for each note name:
| Note Name | Ledger Lines |
|---|---|
| E | 1st above |
| F | 2nd above |
| G | 3rd above |
| C | 1st below |
| B | 2nd below |
| A | 3rd below |
Here are some exercises to practice writing music with treble clef ledger lines:
- Write a melody that uses ledger lines above the staff.
- Write a melody that uses ledger lines below the staff.
- Write a melody that uses ledger lines in both the treble and bass clefs.
Common Queries
What are ledger lines in music notation?
Ledger lines are short lines added above or below the staff to extend the range of notes beyond the five lines and four spaces of the staff.
How do I identify notes on treble clef ledger lines?
To identify notes on treble clef ledger lines, count the lines and spaces from the treble clef sign and apply the letter names of the lines and spaces (EGBDF and FACE).
Why is it important to read music with treble clef ledger lines?
Reading music with treble clef ledger lines is crucial for playing and understanding a wider range of musical compositions, as many notes fall outside the range of the staff.