Lab skills using a graduated cylinder are essential for accurate liquid volume measurement in various scientific disciplines. This guide delves into the techniques, applications, and safety considerations associated with using graduated cylinders, empowering you with the knowledge to obtain precise and reliable measurements in your laboratory endeavors.
Understanding the purpose and importance of using a graduated cylinder sets the foundation for accurate liquid volume measurement. Proper eye level and meniscus reading techniques are crucial for obtaining precise readings, and different types of graduated cylinders cater to specific applications.
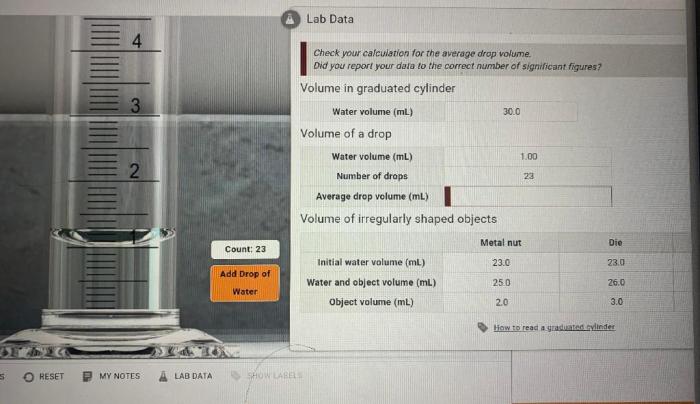
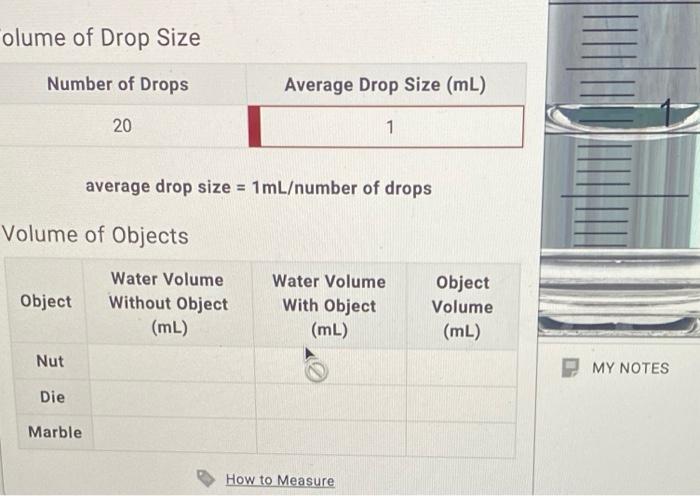
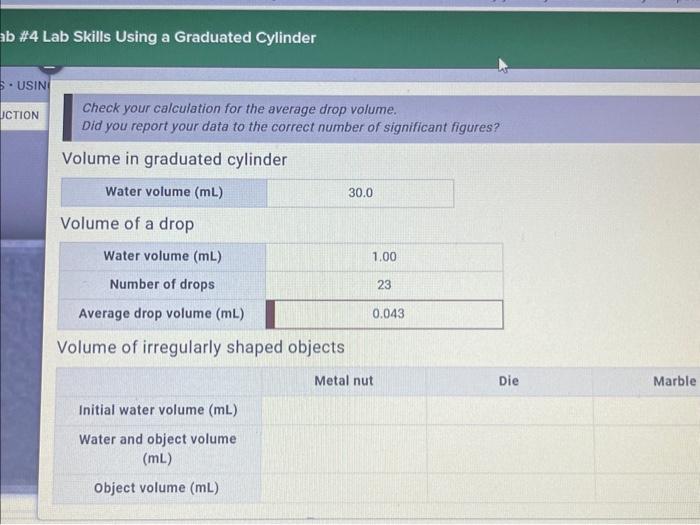
Calibration ensures accuracy, and regular maintenance is essential to maintain reliability.
Measuring Liquid Volume: Lab Skills Using A Graduated Cylinder
Measuring liquid volume accurately is crucial in various scientific experiments and laboratory procedures. A graduated cylinder is a fundamental tool used for this purpose, providing precise volume measurements. Understanding the proper use of a graduated cylinder is essential to ensure reliable and accurate results.
Step-by-Step Instructions for Using a Graduated Cylinder, Lab skills using a graduated cylinder
- Select the appropriate graduated cylinder based on the volume of liquid to be measured.
- Hold the graduated cylinder vertically, at eye level, and ensure that the liquid level is at the same height as your eye.
- Read the liquid level at the bottom of the meniscus (the curved surface of the liquid) to obtain the most accurate measurement.
Types of Graduated Cylinders
- Class A Graduated Cylinders:High-precision cylinders with narrow spouts and calibrated to meet specific accuracy standards.
- Class B Graduated Cylinders:Less precise than Class A cylinders, with wider spouts and less stringent calibration requirements.
- Mohr Pipettes:Similar to graduated cylinders, but with a more precise spout and a calibration mark at a specific volume.
Calibrating a Graduated Cylinder
Calibration is essential to ensure the accuracy of graduated cylinders. It involves comparing the volume indicated by the cylinder with a known volume of liquid.
- Fill the graduated cylinder to the calibration mark with a known volume of liquid using a calibrated pipette or balance.
- Check if the liquid level matches the calibration mark. If not, adjust the calibration of the graduated cylinder accordingly.
- Regular calibration is recommended to maintain accuracy and reliability.
Common Errors in Graduated Cylinder Use
- Parallax Error:Reading the liquid level from an angle, resulting in an inaccurate measurement.
- Meniscus Misreading:Reading the liquid level at the top or bottom of the meniscus instead of the bottom, leading to errors.
- Incorrect Eye Level:Not holding the graduated cylinder at eye level, causing the liquid level to appear higher or lower than it actually is.
To minimize errors, follow proper laboratory procedures, hold the graduated cylinder vertically, and read the liquid level at eye level at the bottom of the meniscus.
Applications of Graduated Cylinders
- Preparing Solutions:Measuring precise volumes of liquids to create solutions with specific concentrations.
- Titrations:Measuring the volume of a titrant added to a solution to determine the concentration of an analyte.
- Calibrating Other Volumetric Equipment:Calibrating pipettes, burettes, and other volumetric glassware using known volumes of liquid.
The appropriate size and type of graduated cylinder should be selected based on the volume and accuracy required for the specific application.
Safety Considerations
- Wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and safety glasses, when handling liquids.
- Handle liquids with care to avoid spills, splashes, or chemical exposure.
- Dispose of liquids and graduated cylinders properly according to laboratory safety protocols.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of calibrating a graduated cylinder?
Calibration ensures the accuracy of volume measurements by adjusting the cylinder’s markings to align with a known volume of liquid.
How can I minimize parallax error when reading a graduated cylinder?
Hold the graduated cylinder perpendicular to your line of sight and bring your eye level to the bottom of the meniscus.
What safety precautions should I take when using graduated cylinders?
Wear appropriate safety gear, handle liquids with care, and dispose of liquids and graduated cylinders safely according to laboratory protocols.