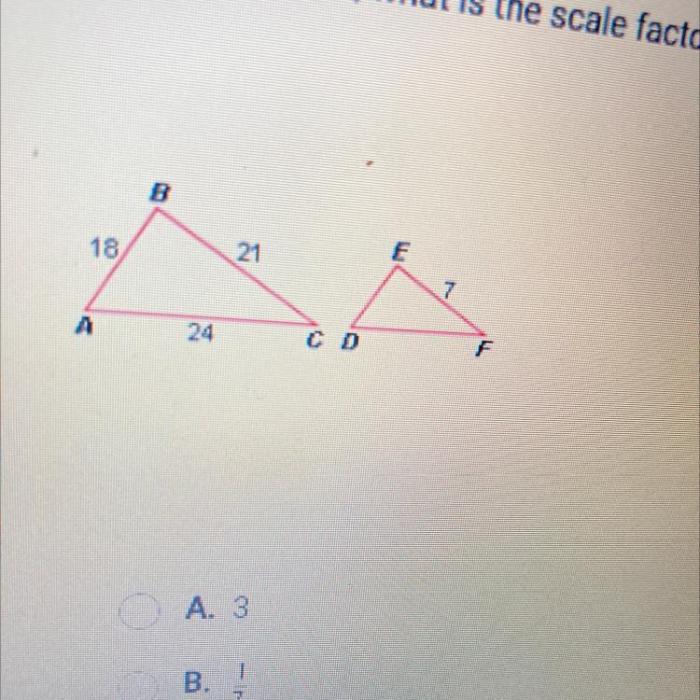
What is the scale factor from abc to def – The concept of scale factor plays a pivotal role in understanding the relationship between original and transformed figures. It provides a mathematical means to quantify the amount of enlargement or reduction applied to a figure, offering insights into its size and shape transformations.
This article delves into the intricacies of scale factor, exploring its definition, methods of calculation, and practical applications in diverse fields such as mapping and engineering. We will also examine the connection between scale factor and similarity, shedding light on how it influences the size and shape of figures.
Definition of Scale Factor
A scale factor is a number that describes the ratio of the size of an object in a drawing or model to its actual size. It is used to enlarge or reduce the size of an object while maintaining its proportions.
Mathematically, the scale factor is defined as the ratio of the length of a line segment in the drawing or model to the length of the corresponding line segment in the actual object.
Calculating Scale Factor
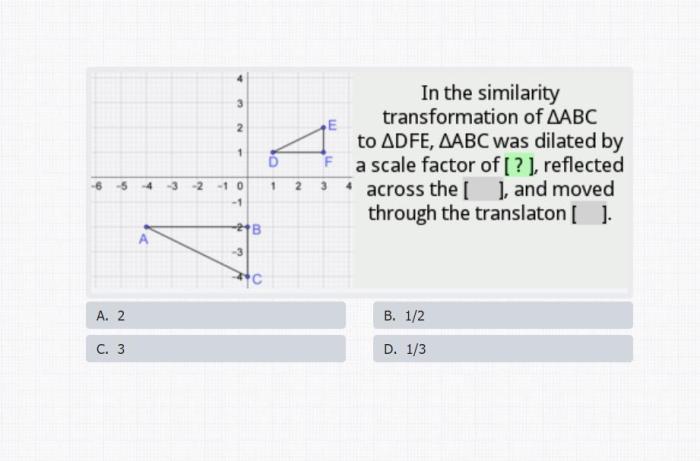
To calculate the scale factor, follow these steps:
- Measure the length of a line segment in the drawing or model.
- Measure the length of the corresponding line segment in the actual object.
- Divide the length of the line segment in the drawing or model by the length of the line segment in the actual object.
The result is the scale factor.
For example, if a line segment in a drawing is 5 cm long and the corresponding line segment in the actual object is 10 cm long, then the scale factor is 5 cm / 10 cm = 0.5.
Applications of Scale Factor
Scale factor has many practical applications, including:
- Mapping: Scale factor is used to create maps that represent large areas on a smaller scale.
- Engineering: Scale factor is used to create models of structures and machines that are too large or complex to build at full size.
For example, a map of the United States might have a scale factor of 1:24,000,000, which means that 1 inch on the map represents 24,000,000 inches in the actual world.
Scale Factor and Similarity
Scale factor is closely related to the concept of similarity. Two figures are similar if they have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. The scale factor between two similar figures is the ratio of the length of a line segment in one figure to the length of the corresponding line segment in the other figure.
For example, a rectangle with a length of 10 cm and a width of 5 cm is similar to a rectangle with a length of 20 cm and a width of 10 cm. The scale factor between the two rectangles is 20 cm / 10 cm = 2.
Examples of Scale Factor
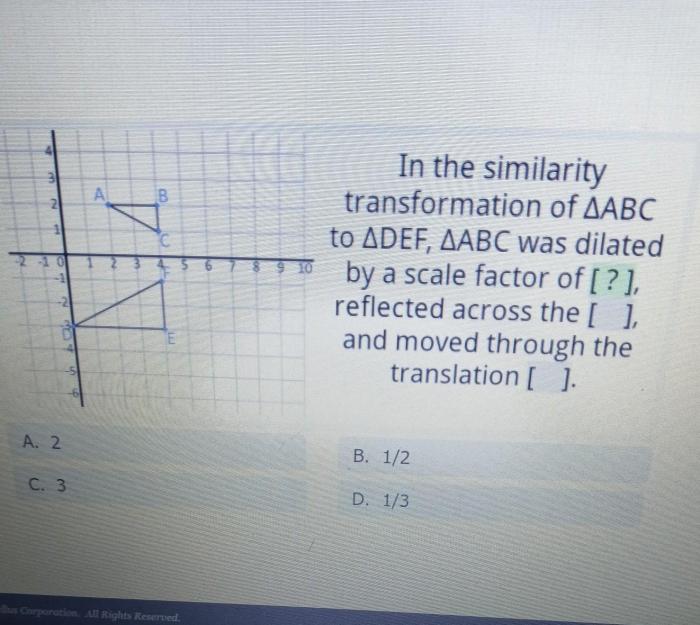
| Original Figure | Scaled Figure | Scale Factor | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Square with a side length of 10 cm | Square with a side length of 5 cm | 0.5 | The scaled figure is half the size of the original figure. |
| Rectangle with a length of 10 cm and a width of 5 cm | Rectangle with a length of 20 cm and a width of 10 cm | 2 | The scaled figure is twice the size of the original figure. |
| Triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 5 cm | Triangle with a base of 5 cm and a height of 2.5 cm | 0.5 | The scaled figure is half the size of the original figure. |
Answers to Common Questions: What Is The Scale Factor From Abc To Def
What is the formula for calculating scale factor?
Scale Factor = Length of Scaled Figure / Length of Original Figure
How does scale factor affect the size of a figure?
Enlarging a figure increases the scale factor, resulting in a larger scaled figure. Conversely, reducing a figure decreases the scale factor, producing a smaller scaled figure.
What is the relationship between scale factor and similarity?
Figures with the same scale factor are similar, meaning they have the same shape but different sizes.