Embark on a captivating journey into the intricate world of plant reproduction with the ‘Flower Structure and Reproduction Worksheet.’ This comprehensive resource delves into the fascinating mechanisms that govern the development and propagation of flowering plants, providing a foundation for a deeper understanding of the natural world.
Through a blend of informative text, engaging diagrams, and interactive exercises, this worksheet unveils the secrets of flower anatomy, pollination, fertilization, and seed dispersal. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of plant life and witness the wonders of nature firsthand.
Flower Structure
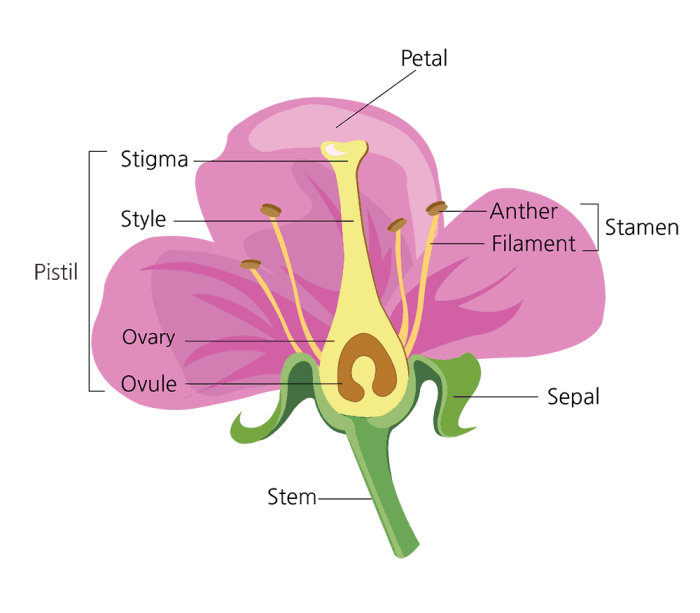
Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants. They consist of several different parts, each with a specific function. The basic structure of a flower includes the sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil.
The sepals are leaf-like structures that form the outermost layer of the flower. They protect the developing flower bud.
The petals are typically brightly colored and attract pollinators. They also help to protect the reproductive organs of the flower.
The stamens are the male reproductive organs of the flower. They consist of a filament and an anther. The filament supports the anther, which produces pollen grains.
The pistil is the female reproductive organ of the flower. It consists of a stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma receives pollen grains, which then travel down the style to the ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules, which can develop into seeds after fertilization.

Flower Reproduction: Flower Structure And Reproduction Worksheet
Flower reproduction involves two main processes: pollination and fertilization.
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower. This can be done by insects, wind, or other animals.
Fertilization occurs when a pollen grain germinates on the stigma and produces a pollen tube. The pollen tube grows down the style to the ovary, where it fertilizes an ovule. This results in the formation of a zygote, which develops into an embryo.
After fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit. The fruit protects the developing seeds and helps to disperse them.
Worksheet Activities
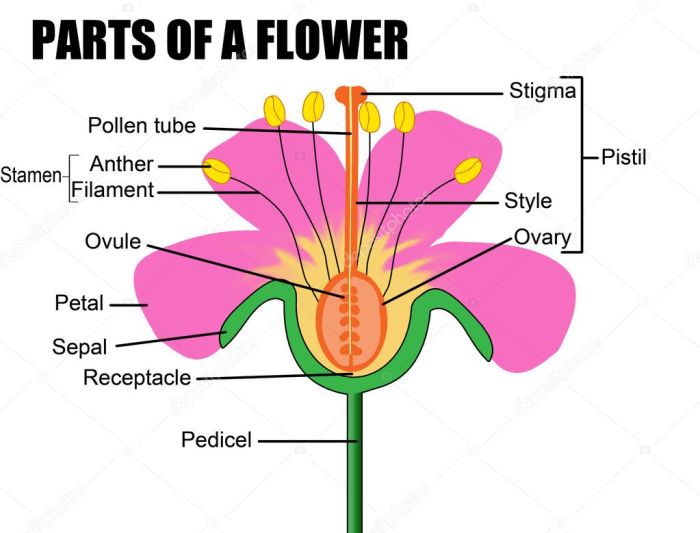
Table: Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Sepals | Protect the developing flower bud |
| Petals | Attract pollinators and protect the reproductive organs |
| Stamens | Produce pollen grains |
| Pistil | Receives pollen grains and contains the ovules |
Diagram of a Flower for Labeling

Questions about Flower Structure and Reproduction
- What are the four main parts of a flower?
- What is the function of the sepals?
- How do pollinators help flowers reproduce?
- What is the difference between pollination and fertilization?
- What is the role of the ovary in flower reproduction?
FAQ Insights
What is the primary function of sepals in a flower?
Sepals primarily serve to protect the developing flower bud before it blooms.
How does pollination occur in wind-pollinated flowers?
In wind-pollinated flowers, pollen grains are dispersed by the wind and carried to the stigma of another flower of the same species.
What is the role of the pistil in flower reproduction?
The pistil, composed of the stigma, style, and ovary, receives pollen grains and facilitates the growth of the pollen tube, leading to fertilization.